Welcome to the rapidly evolving world of manufacturing, where robotic welding innovations play a pivotal role. This article delves into the future of manufacturing by exploring two key questions that encapsulate the excitement and challenges in this dynamic field. The integration of these technologies not only boosts efficiency but also sets a new paradigm for future developments.
How are robotic welding innovations enhancing production efficiency?
1. Automation and Precision
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, precision and consistency are vital. Advanced robotic welding systems have significantly elevated these aspects by automating intricate welding tasks once prone to human error. By leveraging intelligent robotics, manufacturers can achieve unparalleled precision, ensuring that every weld meets strict quality standards.
Moreover, automation reduces the possibility of defects that could lead to costly rework, thereby minimizing waste. By eliminating human fatigue from the equation, robotic welders can maintain consistent performance, enhancing production throughput. These innovations contribute to a reliable production process, upholding the high standards required in modern manufacturing.
Precision in robotic welding not only ensures quality but also allows for the deployment of more complex and intricate designs. As such, manufacturers have the freedom to innovate without the constraints of traditional manual welding limitations. This capability provides a competitive edge in product design and development.
2. Cost Reduction Strategies
While the initial setup of robotic welding systems might be substantial, the long-term cost benefits are compelling. One significant advantage is the reduction in labor costs; robots can operate continuously without breaks, leading to increased productivity and reduced labor expenses. Furthermore, improved efficiency in material usage aids in reducing waste, resulting in cost savings on raw materials.
3. Streamlined Workflow Integration
Integrating robotic welding into existing manufacturing systems can seamlessly enhance workflows. These systems can be customized to sync with current operations, thus minimizing disruption during the transition phase. The adaptability of robotic welding ensures that manufacturers can augment their production without overhauling their entire infrastructure.
Additionally, robotic welding solutions often come equipped with advanced software that enables easy monitoring and control. This integration allows for real-time adjustments, leading to a more agile manufacturing approach. With the ability to quickly respond to production demands, manufacturers can maintain a competitive edge in a fast-paced market.
What challenges do manufacturers face with robotic welding adoption?
1. Initial Investment and Implementation
Moreover, the implementation phase can pose several operational challenges. Current systems may require modifications or complete overhauls to accommodate new technology, which can prolong the integration timeline. This transition period demands meticulous planning and often entails temporary production slowdowns.
Despite these hurdles, many manufacturers recognize the long-term strategic value of investing in robotic welding. By planning and allocating resources effectively, the initial investment can lead to enhanced competitiveness and market positioning. The key is to view the investment as a crucial step toward long-term growth rather than an immediate expense.
2. Skills Gap and Workforce Training
The introduction of robotic welding technology has contributed to a noticeable skills gap in the workforce. Traditional welding techniques differ significantly from automated processes, necessitating specialized training programs. Training initiatives are essential for upskilling the workforce, ensuring they stay relevant in an evolving manufacturing landscape.
Manufacturers often face challenges in sourcing skilled personnel who can operate and maintain robotic systems. To address this issue, partnerships with educational institutions for developing curriculum-focused training can be beneficial. Proactive measures in workforce development can aid in bridging the skills gap, minimizing disruption in the adoption process.
3. Maintenance and Technical Support
Once implemented, robotic welding systems require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance. Preventive maintenance routines are critical for minimizing unexpected downtimes and avoiding costly repairs. Manufacturers need reliable technical support to manage these systems effectively and swiftly address any operational issues that arise.
The future of manufacturing is undoubtedly intertwined with robotic welding innovations. While there are significant advancements improving efficiency, the journey is not without its challenges. Thorough understanding and strategic implementation can help manufacturers navigate this exciting evolution.
Adopting robotic welding technologies presents both opportunities and challenges. Though high initial costs and a skills gap pose hurdles, the benefits of enhanced precision, efficiency, and long-term cost savings are compelling. Manufacturers willing to embrace change and invest in training and maintenance will lead the industry into a new era focused on innovation and excellence.
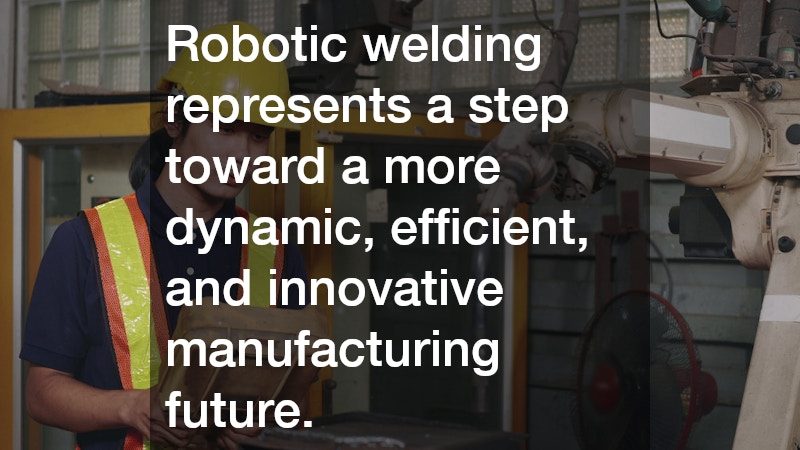
The path toward future manufacturing excellence involves a willingness to adapt and an eagerness to embrace new technologies. By acknowledging the challenges and proactively addressing them, today’s manufacturers can lay the foundation for tomorrow’s industrial leaders. Robotic welding, thus, represents a promising step toward a more dynamic, efficient, and innovative manufacturing future.
.